Effective portfolio management is crucial for maximizing returns while minimizing risks, and one tool that can significantly enhance this process is the TradingView stock heatmap.
Known for its visual representation of stock performance, the heatmap allows traders and investors to monitor market conditions, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best ways to use TradingView’s stock heatmap for portfolio management.
What Is the TradingView Stock Heatmap?
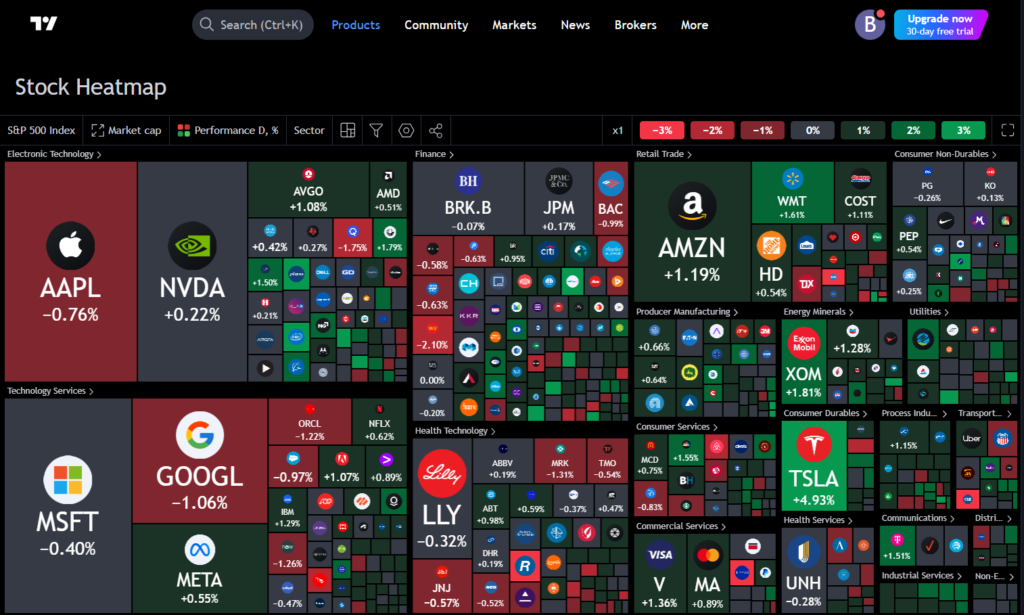
The TradingView stock heatmap is a data visualization tool designed to simplify the monitoring of multiple stocks at once. This tool uses a color-coded system where shades of green indicate positive price changes, and shades of red represent negative ones.
Block sizes correspond to market capitalization, helping users easily identify leading companies in various sectors.By providing a real-time, bird’s-eye view of the stock market, the heatmap allows traders to spot trends, assess sector performance, and even detect volatile stocks that might present opportunities or risks.
Whether you’re a day trader or a long-term investor, the heatmap is a versatile tool for portfolio management.
Setting Up Your Heatmap for Portfolio Management
Before diving into the specifics of how to interpret the stock heatmap, it’s important to set up the tool in a way that aligns with your portfolio management strategy.
- Select Your Market: Begin by choosing the market you want to monitor. The default heatmap often shows U.S. stocks, including key indices like the S&P 500 or NASDAQ. However, if your portfolio includes international stocks or specific sectors, you can adjust the settings to reflect the relevant markets, such as the Nifty 50 for Indian stocks.
- Filter by Sectors: Portfolio management requires diversification, and TradingView’s heatmap allows you to filter stocks by sector. This feature helps you understand how different sectors are performing, enabling you to make informed decisions on whether to increase or decrease your exposure to certain industries.
- Customize for Performance Metrics: For optimal portfolio management, it’s crucial to customize the heatmap based on your key performance metrics—whether you’re looking at percentage price changes, market cap, or even financial ratios like the P/E ratio. This way, you can focus on stocks that meet your investment criteria.
Also Read : How Can TradingView Stock Heatmap Help You Visualize Market Trends?
Interpreting the Stock Heatmap for Portfolio Management
Once your TradingView stock heatmap is set up, interpreting the data is the next step in using it effectively for portfolio management. The heatmap provides real-time updates, and its color and size variations offer valuable insights into stock performance.
1. Color-Coded Performance Indicators
The most immediately noticeable feature of the stock heatmap is its use of color. Shades of green indicate stocks that have gained value, while shades of red signal losses. The intensity of the color reflects the magnitude of the price movement. For instance, a deep green might represent a stock that has increased by more than 5%, while a dark red block could signify a significant loss.
For portfolio management, this quick visual representation helps you identify which stocks or sectors are driving gains or losses in your portfolio. You can quickly assess whether to take profits from outperforming stocks or cut losses in underperforming ones.
2. Block Sizes Indicate Market Cap
In the TradingView heatmap, larger blocks correspond to stocks with a higher market capitalization. This allows you to quickly gauge the market’s heavyweights and their performance. For example, a large block for Apple (AAPL) or Microsoft (MSFT) will dominate the heatmap, indicating these companies’ significant impact on the market.
For portfolio management, this is critical because movements in large-cap stocks can affect entire sectors or markets. If you’re overweight in large-cap stocks, the heatmap helps you determine whether to rebalance your portfolio by shifting some assets into mid-cap or small-cap companies.
3. Sector Groupings for Portfolio Diversification
Diversifying your portfolio across different sectors is a proven strategy for reducing risk. The TradingView heatmap allows you to view stocks based on sector performance, making it easier to identify which industries are thriving and which are struggling.
For example, if the technology sector is predominantly green, it indicates growth in that sector. If your portfolio is heavily invested in tech, you might consider rebalancing by adding stocks from sectors showing signs of recovery, such as energy or utilities. Using the heatmap in this way ensures that your portfolio management strategy remains balanced and diversified.
Also Read: Identify High Volatility Crypto Pairs with Crypto Pairs Screener
Using TradingView’s Heatmap to Analyze Market Trends
The TradingView heatmap is not only useful for monitoring individual stocks but also for identifying broader market trends. By adjusting the heatmap to show historical data, traders can spot patterns that influence portfolio management decisions.
1. Identify Volatility
Volatility presents both risk and opportunity in the stock market. By observing the heatmap’s color intensity, you can identify which stocks are experiencing the most price fluctuations. For instance, deep red or green shades often signify high volatility.
Incorporating high-volatility stocks in your portfolio can lead to higher rewards but also increases risk. For effective portfolio management, you might want to diversify by adding stable, low-volatility stocks that offer a counterbalance to the more volatile assets.
2. Detect Sector-Wide Movements
When several stocks in the same sector exhibit similar price movements, it could indicate a sector-wide trend. For instance, a predominantly green financial sector suggests an upward trend, possibly driven by favorable economic conditions.
For portfolio managers, sector-wide movements offer cues to adjust sector allocations. If the healthcare sector is showing strong performance, you might want to increase your exposure to healthcare stocks to capitalize on the trend.
3. Historical Data for Long-Term Planning
One of the advantages of the TradingView heatmap is the ability to view historical stock performance. This is particularly useful for long-term portfolio management. By observing how a stock has performed over time, you can better assess its long-term potential.
For instance, if a stock has consistently outperformed its sector over several years, it could be a solid long-term addition to your portfolio. Conversely, if a stock’s performance has been erratic, it may not align with a long-term portfolio management strategy.
Also Read: Best ETF Screener Filters For Long-Term Investors
Custom Filters for Targeted Analysis
TradingView’s heatmap also allows for custom filters that can tailor the data to fit your portfolio management goals. You can filter stocks based on criteria such as P/E ratios, dividend yields, or volume.
1. P/E Ratio Analysis
The P/E ratio is an essential tool for assessing a stock’s value. A higher P/E ratio often indicates a stock is overvalued, while a lower P/E suggests it might be undervalued. By setting the heatmap to display stocks by their P/E ratios, you can quickly spot overvalued or undervalued stocks and adjust your portfolio accordingly.
2. Dividend Yield for Income-Oriented Portfolios
If your portfolio management strategy is income-focused, you can filter the heatmap to display stocks by dividend yield. Larger blocks for high-yield stocks allow you to identify income-generating opportunities quickly. This is especially useful for those looking to build a portfolio with consistent cash flow.
3. Volume for Liquidity Analysis
Volume is a key indicator of a stock’s liquidity. Stocks with high volume are easier to trade, while low-volume stocks may be more difficult to buy or sell quickly. Adjusting the heatmap to reflect trading volume can help ensure that your portfolio remains liquid and flexible, a crucial factor in effective portfolio management.
Conclusion
The TradingView stock heatmap is a powerful tool for enhancing portfolio management. Its real-time data visualization simplifies market analysis, allowing traders to identify trends, assess sector performance, and manage risk more effectively. By incorporating this tool into your investment strategy, you can make more informed decisions, ensuring that your portfolio remains balanced and aligned with your financial goals.