Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer a diversified approach to investing, and the ability to identify leading and underperforming ETFs is essential for maximizing profits.
One of the most effective tools for this purpose is the ETF heatmap. Used across various sectors, heatmaps visually represent data, making it easier to analyze the performance of multiple ETFs simultaneously.
This article delves into how ETF heatmaps function and how traders can utilize them to identify high-performing and underperforming ETFs.
What Is an ETF Heatmap?
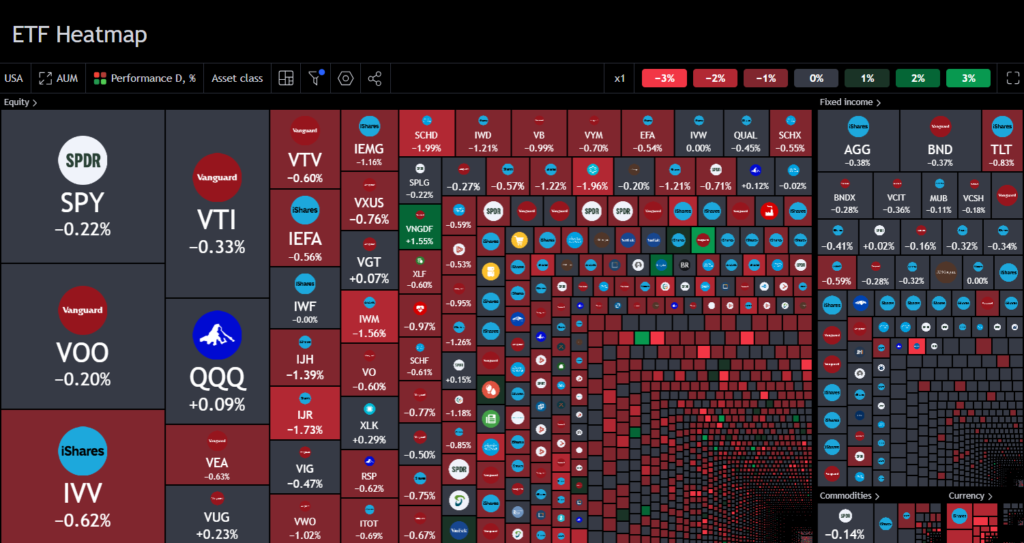
An ETF heatmap is a two-dimensional visual representation that uses color coding to indicate the performance of different ETFs. Each color on the map corresponds to a performance metric, making it easy to spot trends at a glance.
Heatmaps are popular in financial markets, particularly on platforms like TradingView, where investors use them to quickly assess which ETFs are leading or lagging.
Heatmaps have been a staple in data analysis across various industries since the 19th century, evolving into an indispensable tool for traders who want quick insights.
For ETFs, the heatmap consolidates data into a simplified format, allowing investors to instantly identify trends without sifting through complex charts or figures.
Also Read: Best Ways to Use ETF Heatmap For Portfolio Diversification
Understanding the Functionality of ETF Heatmaps
The primary function of an ETF heatmap is to make complex data visually accessible. Different colors represent different performance levels, typically with darker shades indicating leading ETFs and lighter or cooler shades pointing to underperforming ETFs. For example, a green-to-red gradient might indicate the strength or weakness of an ETF over a specific period.
Platforms like TradingView offer ETF heatmaps that allow investors to track market trends in real time. These heatmaps provide crucial information such as price changes, market volume, and percentage gains or losses. This can help investors make informed decisions about which ETFs to hold or trade.
Moreover, ETF heatmaps enable quick comparisons between various sectors, allowing traders to see which industries are flourishing and which are facing challenges. For instance, if tech ETFs are outperforming energy ETFs, a heatmap will make this difference apparent through color contrast.
Also Read: How Can ETF Heatmap Help You Visualize ETF Market Trends?
Identifying Leading ETFs with Heatmaps
One of the key benefits of an ETF heatmap is its ability to highlight leading ETFs. Leading ETFs are those that have consistently shown growth and strong performance relative to the broader market or within their sector.
With a heatmap, these leading ETFs will be displayed in bold or dark colors, making them stand out from the rest. This immediate visual cue allows traders to focus their attention on high-performing ETFs without needing to go through each ETF individually. For instance, if a trader sees that the technology sector is marked in dark green, it signals that tech ETFs are performing well.
Identifying leading ETFs through a heatmap can assist traders in adjusting their portfolios to capitalize on high-growth areas. This enables them to shift capital towards sectors that show promise and avoid lagging sectors.
Spotting Underperforming ETFs
Just as heatmaps help identify leading ETFs, they also reveal underperforming ones. Underperforming ETFs are those that are struggling or losing value over time. These ETFs may be indicated by cooler colors such as blue or light red on the heatmap, signaling a potential downturn.
Spotting underperforming ETFs is crucial for risk management. If a trader’s portfolio includes ETFs that are consistently underperforming, it may be time to sell or reduce exposure to minimize losses. With an ETF heatmap, investors can quickly spot underperforming sectors or individual funds and take necessary action before losses compound.
For instance, if the real estate or energy sectors show signs of weakness on the heatmap, it would allow traders to avoid potential pitfalls. Heatmaps help visualize the comparative performance of these ETFs, offering an easy way to track and monitor market movements.
Also Read: Identify High-Growth Sectors Using TradingView Heatmap
Advantages of Using ETF Heatmaps for Trading Decisions
ETF heatmaps offer several advantages over traditional methods of market analysis. First, they save time. Instead of looking at line charts, bar graphs, or reading through pages of financial reports, traders can view a heatmap and immediately identify the best-performing and weakest ETFs.
Second, heatmaps provide a real-time snapshot of the market. Platforms like TradingView ensure that the heatmaps are updated regularly, giving investors timely insights. This real-time data is especially useful for day traders and short-term investors who need to make quick decisions.
Third, ETF heatmaps offer a visual and intuitive approach. Data is often overwhelming for many traders, but the simplicity of a color-coded system makes it easy to understand even for those who may not be well-versed in advanced financial analysis.
Finally, the comparative nature of heatmaps allows traders to analyze different sectors simultaneously. Whether it’s healthcare, technology, or financials, the heatmap visually represents the relative strength or weakness of each sector in relation to others.
Limitations of ETF Heatmaps
While ETF heatmaps are a powerful tool, they come with limitations. One of the drawbacks is that heatmaps offer a broad view of performance without delving into the details. They show that certain ETFs are leading or underperforming but don’t explain why.
For instance, an ETF might show up as underperforming on the heatmap, but the underlying reasons could be temporary, such as external economic factors or short-term market fluctuations. Traders relying solely on heatmaps may miss out on this context and make hasty decisions.
Additionally, heatmaps only offer a snapshot of the present moment and may not include future forecasts. Investors should use ETF heatmaps as part of a broader strategy that includes fundamental and technical analysis.
Also Read: Visualize Bullish vs Bearish Trends with Stock Heatmap
How to Use TradingView’s ETF Heatmap
Platforms like TradingView provide access to ETF heatmaps that help investors stay on top of market trends. To use TradingView’s ETF heatmap effectively:
- Select Timeframes: Adjust the timeframe to see ETF performance over different periods, whether it’s daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Choose Sectors: Filter heatmaps by sectors to focus on specific industries.
- Analyze Color Patterns: Identify leading ETFs based on the darkest colors and underperforming ones based on lighter shades.
By using these filters and tools, traders can ensure they’re making data-driven decisions that reflect the current market dynamics.
Conclusion
ETF heatmaps offer traders a powerful tool for quickly identifying leading and underperforming ETFs. With the help of color-coded data visualization, investors can make timely and informed decisions to optimize their portfolios.
However, it’s essential to remember that heatmaps should be used alongside other forms of analysis for a comprehensive understanding of market trends. Platforms like TradingView provide easy access to these heatmaps, enabling traders to stay ahead of the curve in the fast-paced world of ETFs.